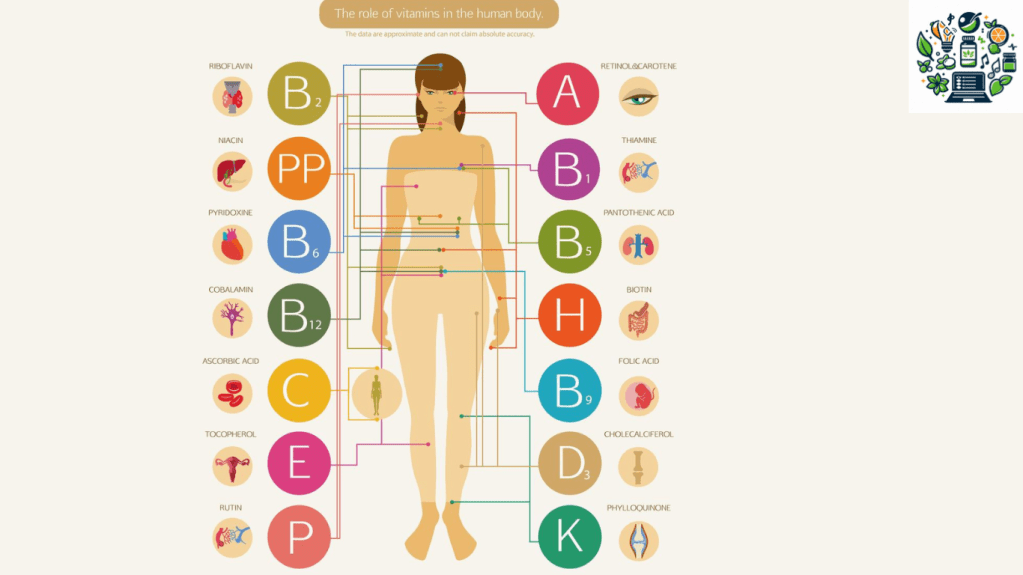
Explore specific vitamins like Vitamin C, D, and Zinc, and explain how they contribute to immune health. Include dietary sources and potential supplements.
Introduction
Your immune system is your body’s defense against infections and diseases. It consists of a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect you from harmful invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. But how can you keep your immune system strong and healthy? One way is to make sure you get enough vitamins from your diet or supplements. Vitamins are essential nutrients that your body needs to perform various functions, including supporting your immune system. In this article, we will explore some of the specific vitamins that are important for immune health, how they contribute to your immunity, and what foods or supplements you can take to get them.
Vitamin C: The Immunity Booster
Vitamin C is a well-known vitamin for its immune-boosting properties. It acts as an antioxidant, protects your cells from damage caused by free radicals, and stimulates the production and function of white blood cells that fight off infections. Vitamin C also enhances the activity of natural killer cells and supports antibody production.
Food Sources: Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes, as well as kiwis, strawberries, papayas, cantaloupes, and pineapples are excellent sources of vitamin C. Vegetables such as bell peppers, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, spinach, kale, and cauliflower are also high in vitamin C.
Supplements: You can take vitamin C supplements in various forms like tablets, capsules, chewables, powders, or liquids.
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
Vitamin D is another key vitamin for immunity. It is a fat-soluble vitamin that can modulate the innate and adaptive immune responses. The innate immune response is the first line of defense against pathogens and involves nonspecific mechanisms, such as physical barriers and inflammation. The adaptive immune response is the second line of defense and involves specific mechanisms, such as the production of antibodies and memory cells. Vitamin D can enhance the function of various immune cells, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, T cells, and B cells. Vitamin D can also regulate the expression of genes that are involved in immune responses.
Sunlight: Vitamin D is mainly produced by your skin when it is exposed to sunlight. However, many factors can affect the amount of vitamin D you make from sunlight exposure, such as the season, time of day, latitude, skin pigmentation, sunscreen use, clothing coverage, and air pollution.
Food Sources: To supplement your vitamin D intake, include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines in your diet. Other foods that contain vitamin D include egg yolks, mushrooms, fortified milk, fortified orange juice, and fortified cereals.
Supplements: Alternatively, you can take vitamin D supplements in the form of tablets, capsules, drops, or sprays.
Zinc: The Immune System Supporter
Zinc is a trace mineral that plays a vital role in immune function. It is involved in the development and activation of various immune cells, such as neutrophils, macrophages, natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells. Zinc also acts as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, and can modulate the expression of genes that are involved in immune responses.
Food Sources: Some of the best food sources of zinc are animal products, such as oysters, beef, pork, chicken, turkey, and eggs. Other foods that contain zinc include legumes, such as beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peanuts. You can also find zinc in nuts, seeds, whole grains, dairy products, and dark chocolate.
Supplements: Alternatively, you can take zinc supplements in the form of tablets, capsules, lozenges, or syrups.
Other Vitamins for Immunity
Vitamin A: The Immune System Enhancer
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that can enhance the function of various immune cells, such as macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells. Vitamin A can also maintain the integrity of the mucous membranes, which are the first line of defense against pathogens.
Food Sources: Some of the best food sources of vitamin A are liver, fish, eggs, dairy products, carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, spinach, and kale.
Supplements: Alternatively, you can take vitamin A supplements in the form of tablets, capsules, or liquids.
Vitamin E: The Antioxidant Defender
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that is a potent antioxidant that can protect your cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. Vitamin E can also modulate the function of various immune cells, such as natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells.
Food Sources: Some of the best food sources of vitamin E are nuts, seeds, oils, avocado, spinach, and broccoli.
Supplements: Alternatively, you can take vitamin E supplements in the form of tablets, capsules, or liquids.
Vitamin B6: The Immune Molecule Regulator
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin that is involved in the synthesis and metabolism of various immune molecules, such as cytokines and antibodies. Vitamin B6 can also regulate the expression of genes that are involved in immune responses.
Food Sources: Some of the best food sources of vitamin B6 are meat, poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, nuts, seeds, bananas, and potatoes.
Supplements: Alternatively, you can take vitamin B6 supplements in the form of tablets or capsules.
Vitamin B12: The Blood and Immune Cell Booster
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for the production and maturation of red blood cells and white blood cells. Vitamin B12 can also support the function of natural killer cells and T cells.
Food Sources: Some of the best food sources of vitamin B12 are animal products, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals.
Supplements: Alternatively, you can take vitamin B12 supplements in the form of tablets, capsules, lozenges, sprays, or injections.
Conclusion: Boosting Your Immunity with Vitamins
Vitamins are important nutrients that can help your immune system fight off infections and diseases. Some of the specific vitamins that are beneficial for immune health are vitamin C, D, zinc, A, E, B6, and B12. You can get these vitamins from a variety of foods or supplements. However, before taking any supplements, you should consult with your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage and avoid any potential interactions or side effects.
Remember that vitamins alone are not enough to keep your immune system strong and healthy. You also need to follow a balanced diet, exercise regularly, get enough sleep, manage stress, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. By taking care of your overall health, you can boost your immunity and prevent or recover from illnesses more effectively.
**References:**
– Carr AC, Maggini S. Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients. 2017;9(11):1211.
– Hemilä H. Vitamin C and infections. Nutrients. 2017;9(4):339.
– Wintergerst ES et al. Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions. Ann Nutr Metab. 2006;50(2):85-94.
– Aranow C. Vitamin D and the immune system. J Investig Med. 2011;59(6):881-886.
– Martineau AR et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2017;356:i6583.
– Prietl B et al. Vitamin D and immune function. Nutrients. 2013;5(7):2502-2521.
– Prasad AS. Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells. Mol Med. 2008;14(5-6):353-357.
– Wessels I et al. Zinc as a gatekeeper of immune function. Nutrients. 2017;9(12):1286.
– Shankar AH, Prasad AS. Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;68(2 Suppl):447S-463S.
– Huang Z et al. Role of vitamin A in the immune system. J Clin Med. 2018;7(9):258.
– Semba RD. Vitamin A and immunity to viral, bacterial and protozoan infections. Proc Nutr Soc. 1999;58(3):719-727.
– Stephensen CB et al. Vitamin A enhances in vitro Th2 development via retinoid X receptor pathway. J Immunol. 2002;168(9):4495-4503.- Lee GY et al. The role of vitamin E in immunity. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1614.
– Meydani SN et al. Vitamin E supplementation enhances cell-mediated immunity in healthy elderly subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;52(3):557-563.
– Wu D et al. Effect of dietary supplementation with black currant seed oil on the immune response of healthy elderly subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;70(4):536-543.

Leave a reply to Balanced Nutrition Diet- The basics you need to know – VITAMINPRO Cancel reply