Are you getting enough vitamin D?
It’s a question many of us ask ourselves, especially during the winter months when sun exposure is limited. Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining healthy bones, supporting the immune system, and even reducing the risk of certain diseases. But did you know that there are different types of vitamin D? Enter vitamin D2 and vitamin D3, two forms of this essential nutrient that are often found in supplements. So, which is more effective for your health? In this article, we’ll explore the differences between vitamin D2 and vitamin D3, their sources, absorption rates, and their potential health benefits. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which form of vitamin D may be the best choice for you. Get ready to grasp some valuable information on this important topic and make an informed decision for your overall well-being.
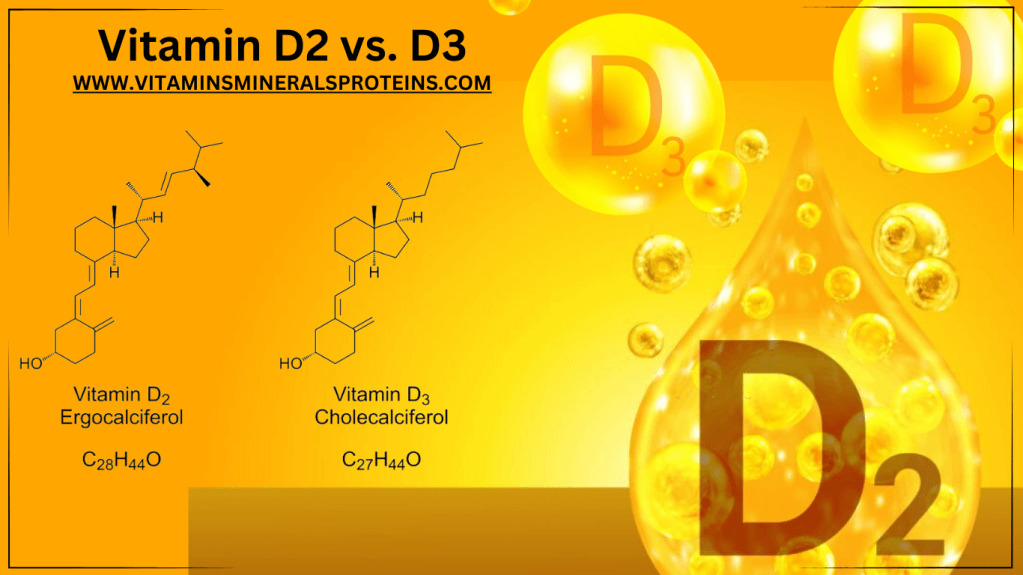
What is Vitamin D2 and how is it different from Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D2, also known as ergocalciferol, it is a type of vitamin D that is synthesized by plants. It is commonly found in fortified foods such as dairy products and cereals. On the other hand, vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol which is synthesized by our skin when it is exposed to sunlight. It can also be found in fatty fish, eggs, and liver.
One key difference between vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 lies in their structure. Vitamin D2 has a slightly different structure compared to vitamin D3, which affects their absorption and utilization in the body. Additionally, vitamin D2 is not as stable as vitamin D3, which means it may have a shorter shelf life in supplements.
In terms of potency, vitamin D3 is considered to be more effective than vitamin D2. Studies have shown that vitamin D3 is better at raising and maintaining blood levels of vitamin D compared to vitamin D2. This is because vitamin D3 is more easily converted into its active form in the body.
It’s important to note that both vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are important for our health. However, if you’re looking for a form of vitamin D that is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body, vitamin D3 may be the better choice for you.
Sources of Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3
Vitamin D2 is primarily found in plant-based sources such as mushrooms that have been exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. Some fortified foods, like milk and breakfast cereals, also contain vitamin D2.
Vitamin D3, on the other hand, is naturally present in a few food sources, including fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna. It is also synthesized in our skin when exposed to sunlight. However, it can be challenging to get enough vitamin D3 from food alone, especially for those who have limited sun exposure or live in areas with less sunlight.
Supplements are a common way to ensure adequate intake of both vitamin D2 and vitamin D3. They come in various forms, such as capsules, tablets, or liquid drops, and can be found in most pharmacies or health food stores.
Absorption and bioavailability of Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3
When it comes to absorption and bioavailability, vitamin D3 has been found to be more effective than vitamin D2. Studies have shown that vitamin D3 is absorbed more easily in the small intestine, making it more bioavailable for the body to use.
The reason for this difference lies in the way vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are metabolized. After absorption, vitamin D3 is converted into its active form, calcitriol, in the liver and kidneys. This active form is responsible for carrying out the various functions of vitamin D in the body. Vitamin D2, on the other hand, undergoes a different metabolic pathway and is converted into a less potent form of vitamin D.
The higher bioavailability of vitamin D3 means that it is more efficiently utilized by the body, leading to higher blood levels of vitamin D. This is particularly important for individuals who have conditions that affect vitamin D absorption, such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease.
Health benefits of Vitamin D2
While vitamin D3 is generally considered more effective, vitamin D2 still offers several health benefits. One of the main roles of vitamin D is to help the body absorb calcium from the diet, which is essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Vitamin D2 has been shown to be effective in raising and maintaining blood levels of calcium, making it beneficial for bone health.
In addition to its role in bone health, vitamin D2 has also been studied for its potential benefits in reducing the risk of certain diseases. Research suggests that vitamin D2 may have anti-inflammatory properties and could play a role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and certain types of cancer. However, more studies are needed to fully understand the extent of these benefits.
Health benefits of Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is widely recognized for its role in maintaining healthy bones and teeth. It helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, two essential minerals for bone health. Sufficient levels of vitamin D3 can help prevent conditions like osteoporosis, which is characterized by weak and brittle bones.
Beyond bone health, vitamin D3 has also been linked to a range of other health benefits. Research suggests that vitamin D3 may play a role in supporting immune function, reducing the risk of autoimmune diseases, and even improving mood and mental health. Some studies have also shown a potential link between vitamin D3 deficiency and an increased risk of certain cancers, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. However, further research is needed to fully understand these associations.
Comparing the effectiveness of Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3 for different health conditions
When it comes to specific health conditions, the effectiveness of vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 may vary. For example, in individuals with vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency, studies have shown that vitamin D3 is more effective at raising and maintaining blood levels of vitamin D compared to vitamin D2.
Similarly, in individuals with conditions such as osteoporosis or osteomalacia, vitamin D3 has been found to be more effective in improving bone health markers compared to vitamin D2.
However, it’s important to note that the optimal form of vitamin D may vary depending on the individual and their specific health needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate form and dosage of vitamin D for your specific situation.
Recommended daily dosage of Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3
The recommended daily dosage of vitamin D can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. The general recommendation for adults is 600-800 international units (IU) of vitamin D per day. However, individuals with certain health conditions or those who have limited sun exposure may require higher doses.
For vitamin D2, the daily intake recommendation is the same as for vitamin D3. It’s worth noting that vitamin D2 is typically prescribed in higher doses compared to vitamin D3 due to its lower potency and bioavailability.
It’s important to remember that exceeding the recommended dosage of vitamin D can lead to toxicity, which can have adverse effects on health. Therefore, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Vitamin D2 vs. Vitamin D3: Which is better for different population groups?
Certain population groups may have specific considerations when it comes to vitamin D supplementation. For example, individuals with limited sun exposure, such as those who live in northern latitudes or are homebound, may benefit from vitamin D supplementation.
In individuals with conditions that affect vitamin D absorption, such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, vitamin D3 may be very much more effective due to its higher bioavailability.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women may also have increased vitamin D requirements. Vitamin D3 is often recommended for these groups, as it has been shown to be more effective at maintaining adequate vitamin D levels in both the mother and the developing baby.
Ultimately, the choice between vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 should be based on individual circumstances and the guidance of a healthcare professional. They can assess your specific needs and determine the most appropriate form and dosage of vitamin D for you.
Conclusion: Choosing the right form of Vitamin D for your health needs
In summary, both vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are important to our overall health and well-being. However, if you are looking for a form of vitamin D that is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body, vitamin D3 may be a better choice. It has been shown to have greater bioavailability and potency in increasing and maintaining blood levels of vitamin D compared to vitamin D2.
Nonetheless, vitamin D2 offers some health benefits, especially bone health and reduced risk of certain diseases. It is commonly found in fortified foods and plant sources. If you are considering vitamin D supplementation, it is important to consult with your doctor to determine which form and dosage will best suit your specific needs. Factors such as general health, sun exposure, and underlying medical conditions can be taken into account when making a decision. Remember that maintaining proper vitamin D levels is essential to your health. So don’t hesitate to seek professional advice to ensure you’re getting adequate vitamin D for your overall health.
References :
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(3):266-281. doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
- Bouillon R, Carmeliet G, Verlinden L, et al. Vitamin D and human health: Lessons from vitamin D receptor null mice. Endocr Rev. 2008;29(6):726-776. doi:10.1210/er.2008-0004
- Rosen CJ. Clinical practice. Vitamin D insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(3):248-254. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1009570
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al., editors. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press (US); 2011. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/

Leave a comment